You can write and run your C++ unit tests by using the Test Explorer window. It works just like it does for other languages. For more information about using Test Explorer, see Run unit tests with Test Explorer.
Some features such as Live Unit Testing, Coded UI Tests and IntelliTest aren't supported for C++.
Visual Studio includes these C++ test frameworks with no extra downloads required:
You can use the installed frameworks, or write your own test adapter for whatever framework you want to use within Visual Studio. A test adapter integrates unit tests with the Test Explorer window. Several third-party adapters are available on the Visual Studio Marketplace. For more information, see Install third-party unit test frameworks.
Visual Studio 2017 and later (Professional and Enterprise)
C++ unit test projects support CodeLens.
Visual Studio 2017 and later (all editions)
Earlier versions of Visual Studio
You can download the Google Test adapter and Boost.Test Adapter extensions on the Visual Studio Marketplace. Find them at Test adapter for Boost.Test and Test adapter for Google Test.
You can also use Copilot /tests slash command to generate unit tests from code. For example, you can type /tests using Boost framework to generate Boost.Test tests. For more information, see Use slash commands in Copilot Chat.
The following sections show the basic steps to get you started with C++ unit testing. The basic configuration is similar for both the Microsoft and Google Test frameworks. Boost.Test requires that you manually create a test project.
Define and run unit tests inside one or more test projects. A test project creates a separate app that calls the code in your executable and reports on its behavior. Create test projects in the same solution as the code you want to test.
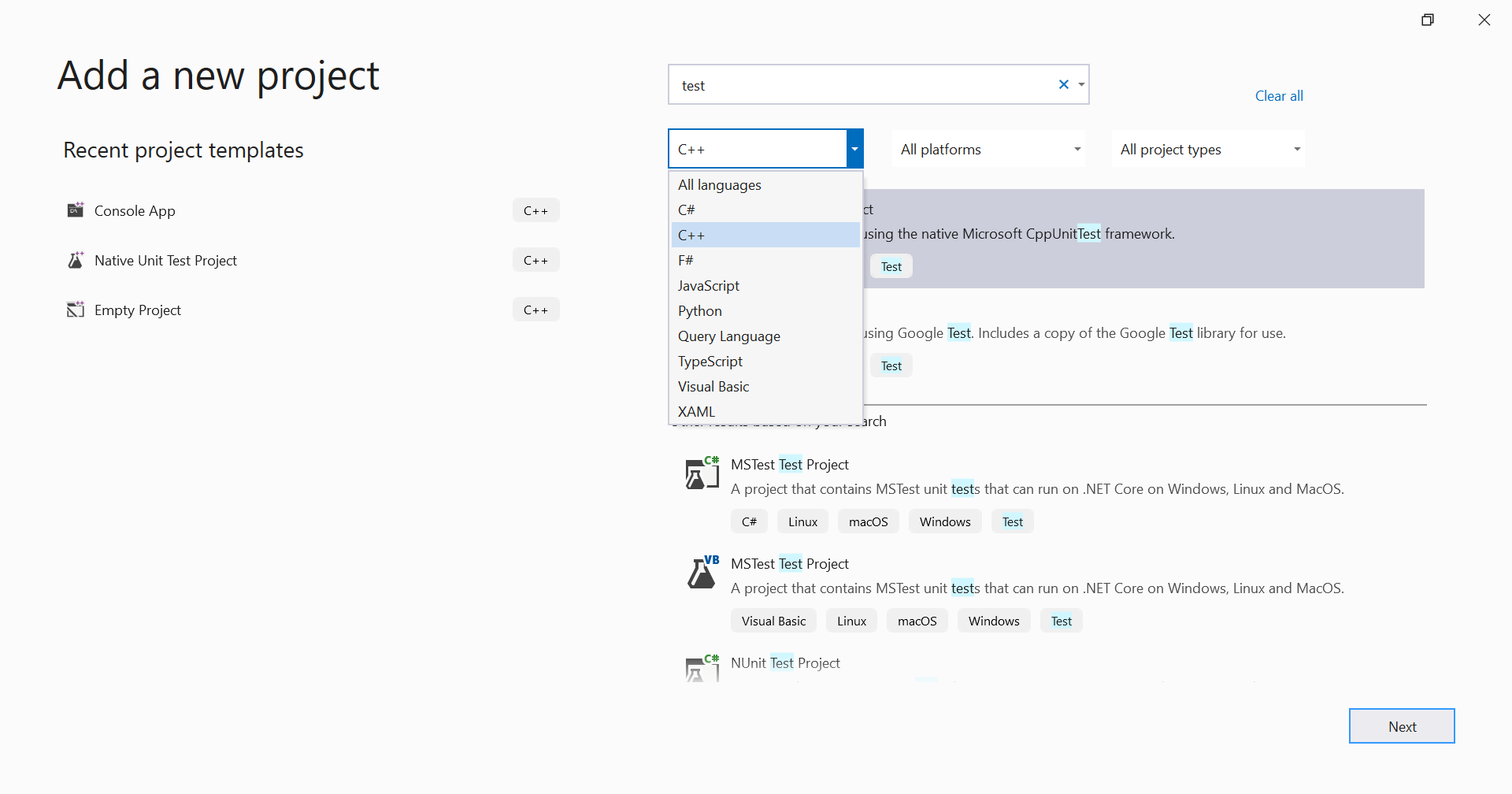
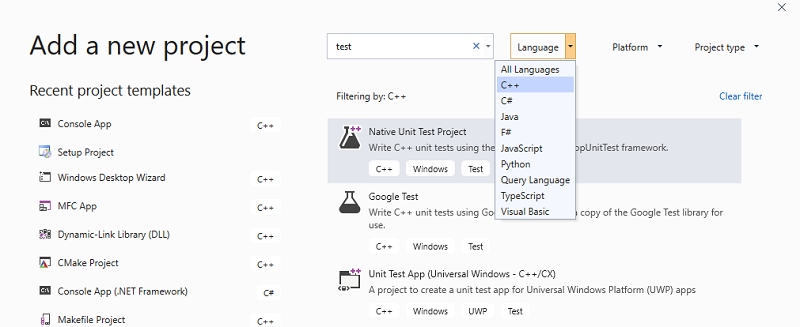
To add a new test project to an existing solution,

Define and run tests inside one or more test projects. Create the projects in the same solution as the code you want to test. To add a new test project to an existing solution,
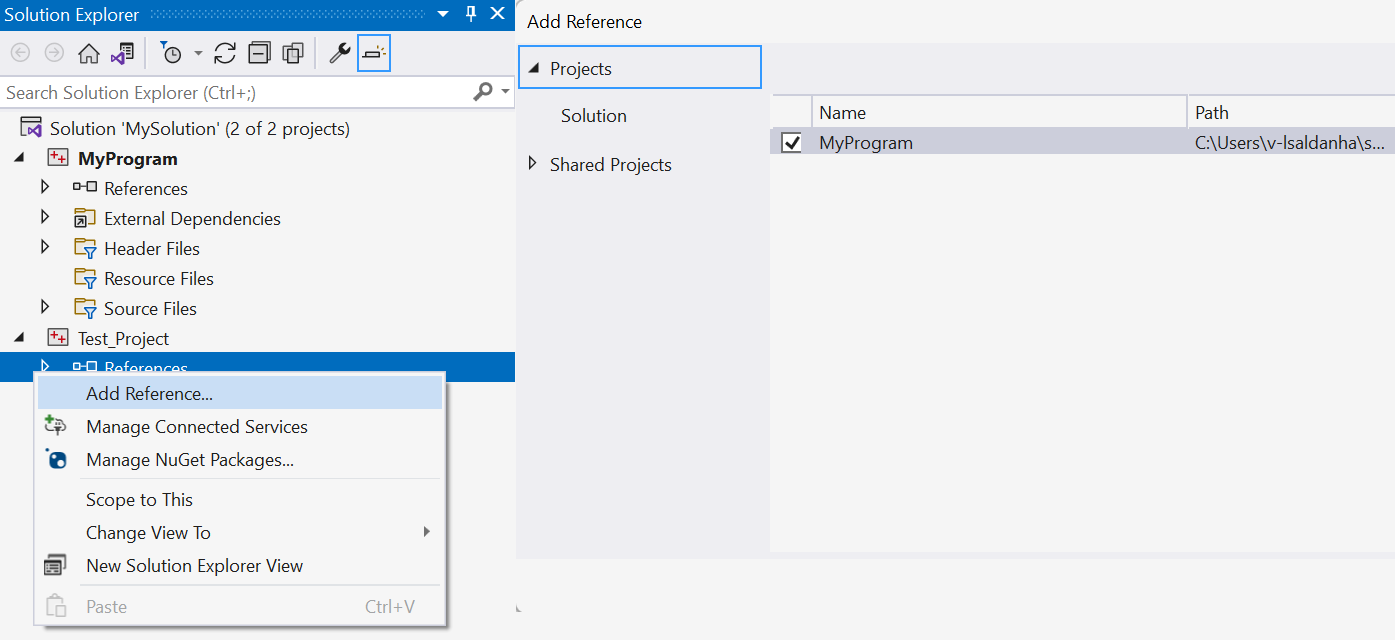
To enable access to the functions in the project under test, add a reference to the project in your test project. Right-click on the test project node in Solution Explorer for a pop-up menu. Choose Add > Reference. In the Add Reference dialog, choose the project(s) you want to test.
If the test code doesn't export the functions that you want to test, add the output .obj or .lib files to the dependencies of the test project. For more information, see To link the tests to the object or library files. Don't include object files that have a main function or another standard entry point such as wmain , WinMain , or DllMain . When you add new source files to your project, update the test project dependencies to include the corresponding object files.
Next, in your unit test .cpp file, add an #include directive for any header files that declare the types and functions you want to test. Type #include " , and then IntelliSense activates to help you choose. Repeat for any more headers.
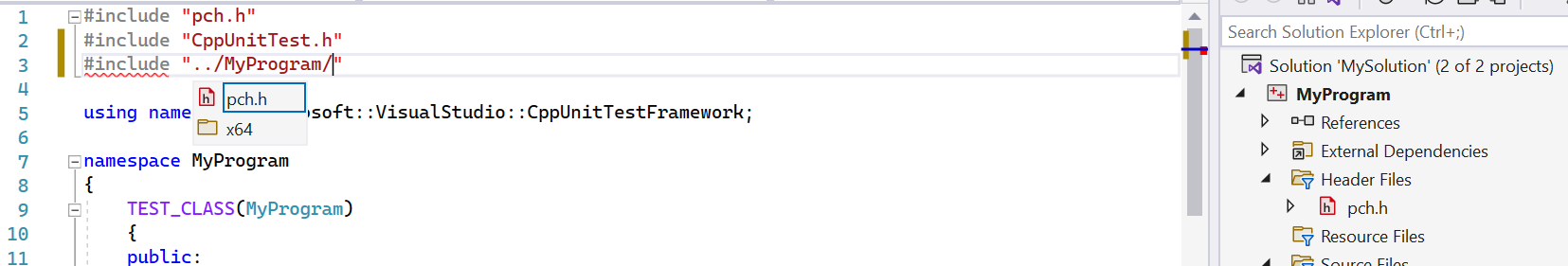
To avoid having to type the full path in each include statement in the source file, add the required folders in Project > Properties > C/C++ > General > Additional Include Directories.
This section shows syntax for the Microsoft Unit Testing Framework for C/C++. It is documented here: Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.CppUnitTestFramework API reference. For Google Test documentation, see Google Test primer. For Boost.Test, see Boost Test library: The unit test framework.
The .cpp file in your test project has a stub class and method defined for you. They show an example of how to write test code. The signatures use the TEST_CLASS and TEST_METHOD macros, which make the methods discoverable from the Test Explorer window.
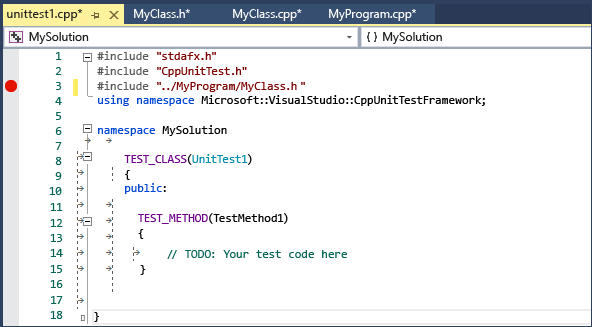
TEST_CLASS and TEST_METHOD are part of the Microsoft Native Test Framework. Test Explorer discovers test methods in other supported frameworks in a similar way.
A TEST_METHOD returns void. To produce a test result, use the static methods in the Assert class to test actual results against expected results. In the following example, assume MyClass has a constructor that takes a std::string . This example shows how you can test that the constructor initializes the class the way you expect:
TEST_METHOD(TestClassInit)
In the previous example, the result of the Assert::AreEqual call determines whether the test passes or fails. The Assert class contains many other methods to compare expected results with actual results.
You can add traits to test methods to specify test owners, priority, and other information. You can then use these values to sort and group tests in Test Explorer. For more information, see Run unit tests with Test Explorer.
Note CTest integration with Test Explorer is not yet available. Run CTest tests from the CMake main menu.
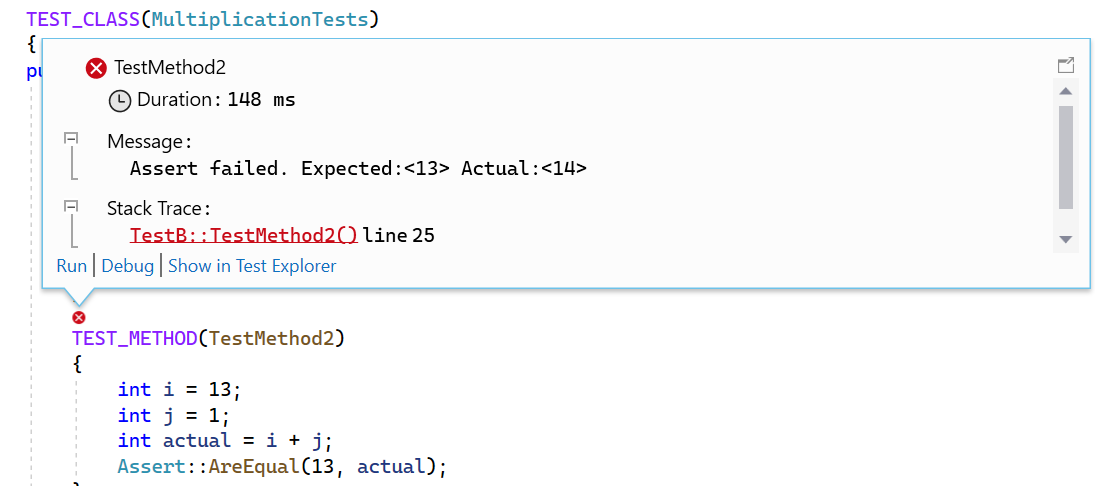
For failed tests, the message displays details that help to diagnose the cause. Right-click on the failing test for a pop-up menu. Choose Debug to step through the function where the failure occurred.
For more information on using Test Explorer, see Run unit tests with Test Explorer.
For more information on unit testing, see Unit test basics.
Visual Studio 2017 and later (Professional and Enterprise editions)
CodeLens lets you quickly see the status of a unit test without leaving the code editor.
Initialize CodeLens for a C++ unit test project in any of the following ways:
After it's initialized, you can see the test status icons above each unit test.
![]()
Choose the icon for more information, or to run or debug the unit test: